installation of heat pump ventilation and heat recovery ventilation
One
of the main components of the ventilation system, is the ductwork that
transports the air. The system is individually designed to the
structural conditions and layout of the property.

We recommend rigid metal safe-seal duct for maximum efficiency, health
benefits and durability. To ensure maximum heat recovery and virtually
silent operation, high quality thermal insulation and acoustic duct is
used. In limited spaces such as ceiling voids or barn conversions, where
there is exposed roof structure, special low-profile flat metal duct can be
specified. The ductwork can usually be hidden quite easily around the
house. For heat recovery ventilation systems installed in a renovation, it is sometimes prudent to use radial plastic duct with a 90mm diameter. However, two or more ducts may need to be installed per room to obtain the necessary airflow. There are several types of duct available and we have highlighted their advantages and disadvantages in this document, so that you can easily undertand the advantages of rigid metal safe-seal ducting.
For an installation manual, please visit our downloads section.
The Loft
This
is normally an area where you can run the ductwork freely from the ventilation appliance to the ceiling terminals in the ceiling of the floor
below (usually the first floor). The duct is usually at a 200mm/250mm
diameter at this stage coming straight off the appliance and it will
reduce down to 100mm/125mm to be connected to the ceiling terminals.
If
you are using the loft as habitable space as well, hopefully there will
be some dead space created on either side, by the pitch of the roof.
Check the specification of the ventilation appliance that you think is
suitable for your property, to work out the minimum space required. For
access to clean the filters, it will be best to leave approximately
600mm in front of the appliance, or integrate an access door within the
wall so that the appliance remains accessible.
The best location is to have a dedicated PLANT ROOM, but alternative
locations for the appliance can be in large cupboards, loft or perhaps in
your utility room.
Although
a ventilation appliance from Total Home Environment runs pretty much silently, if it has to be located in a loft, you will usually
locate it above a bathroom or dressing room, to minimise the risk of
noise caused by vibration. The ventilation appliance should be mounted on
plenty of insulation on top of the joists, or on the wall. The
appliances weigh between 40-225kg, but it is best to check the
specification sheet for the exact weight of the appliance, to ensure the
surface it is to be mounted on, will have a satisfactory weight-bearing
capacity.
The
appliance will produce approximately 3-5 litres of moisture in the
winter months, so you will need to fit a condensate pipe to a trap
linked to your internal waste water pipe.
You
need to be aware of where you can locate the two louvres, for the
fresh-air intake and stale-air outtake. These need to be placed a
MINIMUM of 3m apart horizontally or 1m apart vertically to stop
cross-contamination. They can be located on the gable end of the loft
area, under the eaves or you can have special roof vents which your
roofing contractor can supply you with.
Will the property have a warm roof or a cold roof? This is very important to establish with your architect or builder
before we complete a quote for you, as it will effect the insulation
properties of the ductwork that may run in this area.
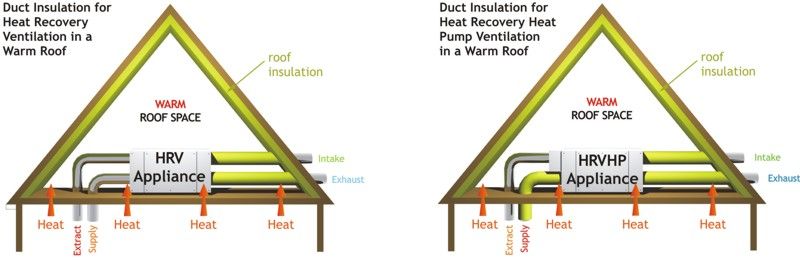
A warm roof is where the insulation is placed in the roof
itself, therefore making the roof area warm. If insulation is only going
to be placed in the floor of the loft area, this is known as a cold
roof as the loft area will be cold in comparison to the rest of the
house.
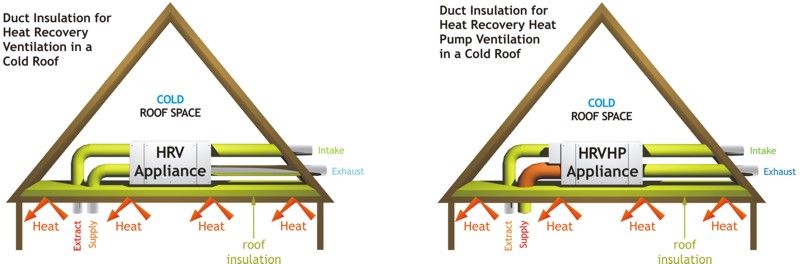
If you have a cold roof construction the extracted air ducts
from kitchens and bathrooms and the supply air ducts to the habitable
rooms of the house will need to be well insulated where they are in the
loft area. This will obviously increase the cost of the quotation so
that more insulation can be accounted for.
Duct Route

Rigid metal ventilation ductwork
In
the ceiling voids, you will mainly have to run the ductwork with the
joists, unless of course your floor construction allows for ductwork to
go through it, ie posi joists or i-beams. Always check with your builder or
surveyor where holes can be made and how big they can be through any joist structure.

PVC flat channel ventilation ductwork
To drop down to the lower floors you can utilise the following spaces:
- soil-pipe boxing or existing boxing-in
- airing cupboard
- boiler cupboard
- fitted wardrobe
- coats cupboard

Ceiling Terminals
The ideal place for locating ceiling terminals is opposite a
door but next to a window, so you create air circulation. Of course when
you get downstairs or to the lower floors, you are more restricted on
where you can put the terminals, as you will be channelled by your
route.

Most
of the time, the terminals downstairs are likely to be at the corners
of the room where the voids to drop the ductwork down, are likely to be
above.
Occasionally
you can use low profile duct to drop down a timber partition, but for
airflow purposes, it is best to restrict the use of this flat channel
ducting as much as possible.
Wiring-Up
The
ventialtion appliance itself would normally need to be wired into your house
electrics by a qualified electrician, although if you have an
electrical socket nearby you may be able to just plug in there. It will
be best to speak to your electrician first.
The
controller should be placed in a hallway or landing where you will have
convenient access to alter the program or put the system on boost. Low
voltage cable needs to run from the controller to the ventilation appliance and any PTC heated ceiling terminals you may have (HPV Series) system only).